Exploring the Efficacy of Reconstructive Techniques in Peri-Implantitis Treatment: A Systematic Review
In a world where dental health is paramount, the latest systematic review and meta-analysis published in Acta Odontologica Scandinavica offers invaluable insights into peri-implantitis treatment. The study, titled “The effect of reconstructive techniques as treatment modality for peri-implant osseous defects,” compares conventional peri-implant flap surgery with reconstructive surgical techniques, shedding light on their effectiveness in treating this prevalent dental issue.
Understanding Peri-Implantitis and Its Impact
Peri-implantitis represents a significant challenge in dental implant care. It’s characterized by an inflammatory response leading to the loss of supporting bone around an implant. The etiology of peri-implantitis is multifactorial, involving bacterial infections, biomechanical factors, and patient-specific factors like systemic health and oral hygiene practices. The complexity of peri-implantitis lies not just in its prevention but also in its management, especially when bone loss has occurred.
Reconstructive Techniques: A New Hope in Treatment
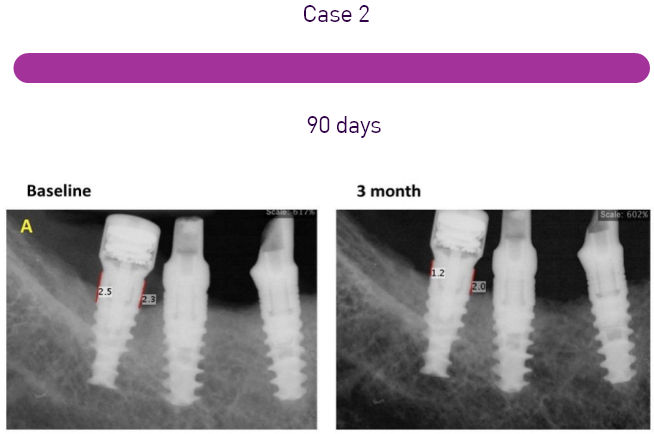
The systematic review by Risolo et al. sheds light on the effectiveness of reconstructive surgical techniques in treating peri-implant osseous defects compared to conventional peri-implant flap surgery. The study analyzed data from nine published articles involving 442 patients. It was found that reconstructive techniques showed a greater extent of defect fill compared to conventional surgical methods. However, when it comes to clinical measures of peri-implant disease, such as bleeding on probing and reduction of probing depth, no significant differences were observed between open flap debridement and regenerative surgery over a 12-month period.
The Significance of Bone Regeneration in Peri-Implantitis
Bone regeneration plays a crucial role in the treatment of peri-implantitis, especially when there is significant bone loss. The goal of regenerative therapies is to restore the lost supporting bone, thereby stabilizing the implant and improving its prognosis. Various techniques and materials are used in bone regeneration, including bone grafts, barrier membranes, and growth factors. The choice of technique often depends on the extent of the defect and the specific clinical scenario.
Challenges and Considerations in Reconstructive Techniques
While reconstructive techniques have shown promise in bone defect filling, they are not without challenges. One of the key considerations in their application is the selection of suitable candidates. Factors such as the patient’s systemic health, smoking status, oral hygiene practices, and the configuration of the bone defect must be taken into account. Additionally, the skill and experience of the clinician play a vital role in the success of these procedures.
Aesthetic Considerations in Peri-Implantitis Treatment
Apart from functional outcomes, aesthetic considerations are becoming increasingly important in peri-implantitis treatment. Patients are concerned not only about the stability and longevity of their implants but also about the appearance of their gums and teeth. Regenerative procedures, while primarily aimed at bone regeneration, may also have positive aesthetic outcomes by improving the contour and volume of the peri-implant soft tissues. However, further research is needed to confirm these aesthetic benefits and to develop protocols that optimize both functional and aesthetic outcomes.
The Future of Peri-Implantitis Treatment
The field of peri-implantitis treatment is rapidly advancing, with ongoing research into new materials, techniques, and protocols. Future studies are expected to focus more on patient-centered outcomes, including aesthetic considerations and quality of life. Additionally, there is a growing interest in minimally invasive techniques that can reduce patient morbidity and improve recovery times.
In conclusion, the treatment of peri-implantitis, especially in the context of osseous defects, is a complex and multifaceted challenge. The latest systematic review highlights the potential of reconstructive techniques in improving bone defect filling. However, it also underscores the need for a comprehensive approach that considers both clinical and aesthetic outcomes.
As research in this field continues to evolve, it is expected that new insights and innovations will further enhance the management of this challenging condition, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.